The History of Classic Casinos: From 17th-Century Europe to Modern Entertainment

Casinos have long been synonymous with glamour, excitement, and risk-taking. But behind the glittering lights of Las Vegas or the high-tech casinos in Macau lies a fascinating story that stretches back centuries. The history of classic casinos begins in Europe during the 17th century and has evolved into today’s billion-dollar entertainment industry.
Early Beginnings: The Birth of the Casino in Europe
The word casino comes from the Italian term casa, meaning “house.” In its earliest form, the word referred to small villas or social clubs where people gathered for music, dancing, and socializing. Over time, these houses also became associated with gambling activities.
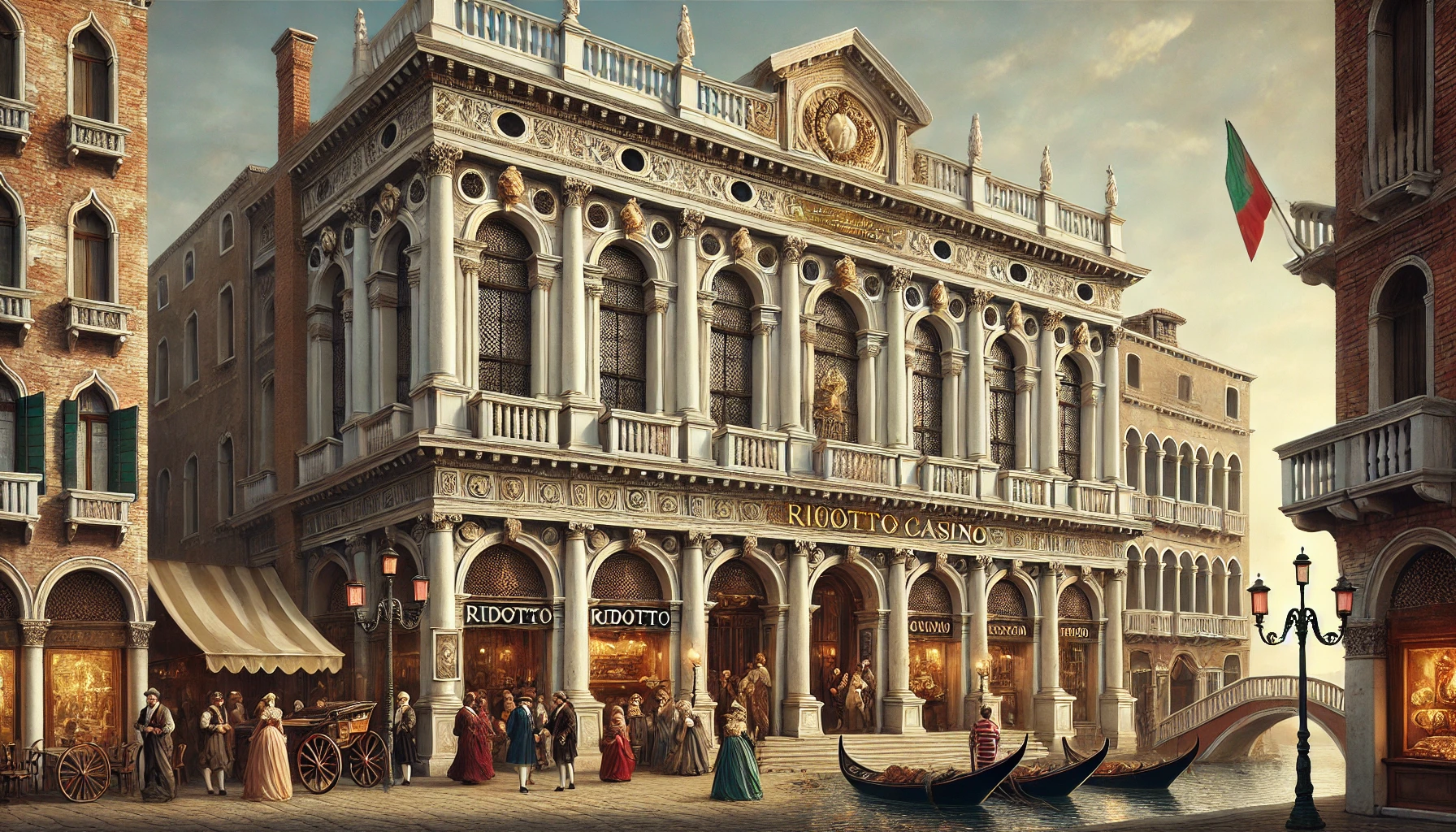
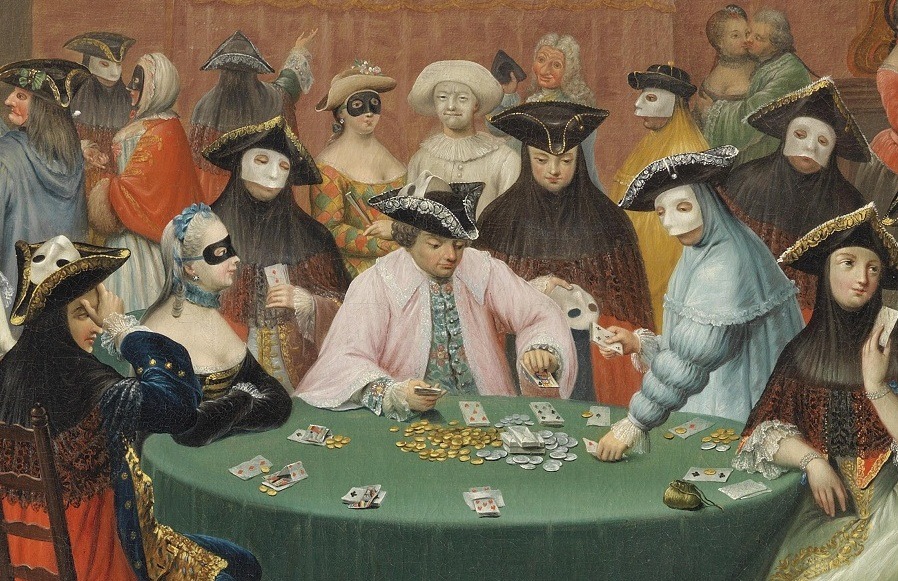
The world’s first recognized gambling house was the Ridotto, established in Venice, Italy, in 1638. Created by the Venetian government to provide controlled gambling during the carnival season, the Ridotto was housed in the Palazzo Dandolo and offered a safe, regulated environment for gaming. It introduced structured games like bassetta and biribi, which were popular among the aristocracy. The Ridotto set the precedent for what would later become the classic casino model.
Expansion Across Europe

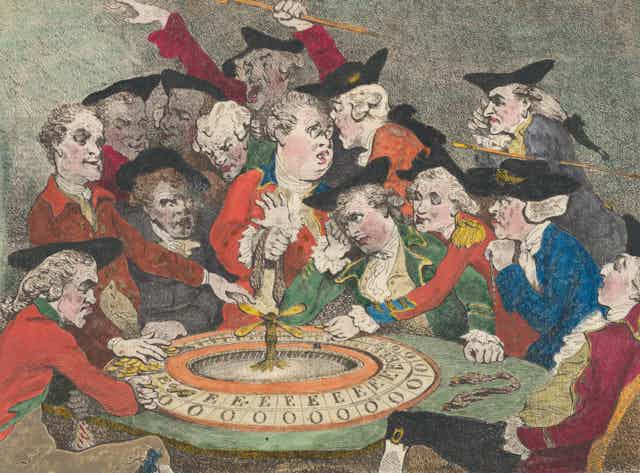
By the 18th and 19th centuries, gambling houses began to spread across Europe. Cities like Paris, Baden-Baden, and Monte Carlo became famous destinations for Europe’s elite.
• France contributed games that are still central to casinos today, such as roulette and blackjack (then known as vingt-et-un). Roulette, invented in the 18th century, quickly became the centerpiece of gambling establishments.
• Germany saw the rise of spa towns like Baden-Baden and Wiesbaden, where elegant casinos attracted wealthy visitors seeking both leisure and gaming.
• Monaco, particularly Monte Carlo, became iconic in the 19th century with the establishment of the Casino de Monte-Carlo in 1863. Its lavish architecture and connection to European royalty gave gambling a glamorous image.
These European gambling houses were not just centers of play; they were cultural landmarks, mixing luxury, architecture, and social prestige.
The Rise of Gambling in America

Casinos made their way to the United States in the 19th century, particularly during the expansion of the frontier. Unlike Europe’s aristocratic gambling houses, American gambling was often associated with saloons in the Wild West, where card games like poker and faro flourished.
By the early 20th century, gambling had become a controversial issue, with most states banning it. However, in 1931, Nevada legalized gambling to combat the effects of the Great Depression. This move laid the foundation for Las Vegas to become the gambling capital of the world.
Las Vegas and the Golden Age of Casinos

The development of Las Vegas during the mid-20th century marked the golden age of classic casinos. Luxurious resorts like the Flamingo, Sands, and Caesars Palace combined gambling with entertainment, fine dining, and shows by legendary performers like Frank Sinatra and Elvis Presley.
Las Vegas redefined the casino as more than just a place to gamble—it became a full-scale entertainment destination. The image of neon lights, bustling slot machines, and high-stakes poker games became synonymous with the city.
Casinos in Asia and Global Expansion
By the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the casino industry expanded beyond Europe and the United States. Asia, particularly Macau, rose as a global powerhouse in gambling. In 2002, Macau liberalized its casino industry, attracting international operators and transforming the city into the world’s largest gambling hub, surpassing even Las Vegas in revenue.
Singapore also entered the scene with the opening of integrated resorts like Marina Bay Sands and Resorts World Sentosa, blending gambling with luxury shopping, hotels, and cultural attractions.
The Modern Casino Experience
Today’s casinos blend tradition with cutting-edge technology. Classic games like roulette, blackjack, and poker remain staples, but they are now enhanced with electronic tables, live dealers broadcast online, and immersive digital platforms.
Casinos have also embraced non-gaming elements to attract a wider audience. Fine dining, concerts, theaters, shopping malls, and even theme parks are part of the modern casino complex. The focus is not solely on gambling but on creating a holistic entertainment experience.
Online casinos and mobile gaming platforms have further expanded accessibility, allowing players to experience classic casino games from anywhere in the world. This digital shift demonstrates how far the concept of the casino has evolved from its 17th-century Venetian origins.
Conclusion: From Exclusive Clubs to Global Icons
From the Ridotto in 1638 Venice to the neon-lit resorts of Las Vegas and the modern integrated resorts in Asia, the history of casinos reflects both cultural change and technological innovation. What began as exclusive houses for Europe’s elite has transformed into a global industry that combines gambling with luxury, entertainment, and cutting-edge technology.
While the essence of risk and reward remains unchanged, the casino of today is more than a gambling hall—it is a cultural phenomenon, shaping tourism, architecture, and even popular imagination. The classic casino continues to evolve, proving that the thrill of chance will always hold a timeless allure.